One of the main difficulties in connecting old and remote equipment is wiring. In the case of indoor applications, pipes and cables must be installed to the equipment to be connected. In general, this method proves very complex and above all very costly. Outside, it is necessary to dig trenches, to bury the cables but before obtaining authorizations, which is often tedious. Besides, if the equipment to be connected is on the other side of a major traffic artery or parking lot, the cost increases and the licenses to be obtained multiply. Often, it is simply impossible to install pipes between water pumps, generators or chillers and the control room. Hence, how to access the data of the desired equipment?
Consider the traditional method of installing a distributed I / O system wirelessly with Ethernet radios. However, this is a complicated operation, resulting in periods of inactivity that are always expensive. Thanks to ProSoft Technology's wireless I / O system, the costs are lower and the shutdown times disappear altogether.
What is the difference between wireless I / O and conventional Distributed I / O with Ethernet radios?
The second system, using Ethernet radios, requires operators in the field to support network communications and to program a data communication network. With ProSoft Technology's wireless I / O, this operation is unnecessary.
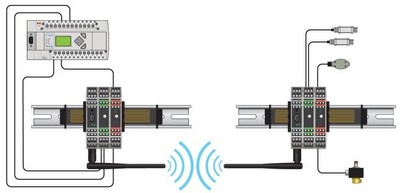
Also known as "wireless terminals", wireless I / O provides a simpler method of communication, designed to establish reliable and secure connections. Unlike data radios, the wireless I / O system requires no programming software or network protocols to configure. Wireless I / O radios are sold in pairs already programmed to connect with each other. The I / O signal sent between the radios uses 128-bit AES encryption to ensure that only the other coupled radio can read the information. Each I / O module reads the machine's physical signals - 24 VDC digital signals and 0 - 10 V or 4 - 20 mA analog signals - and then sends this information to the I / O module corresponding to the other termination . The corresponding module simply reproduces the signal on its output terminals. The digital I / O module has four inputs and four outputs, while the analog modules have two inputs and two outputs. The system is bidirectional, which means that each radio can send inputs and receive outputs. Each pair of radios can support 16 pairs of I / O modules, including 64 digital inputs and outputs or 32 analog inputs and outputs.
Given the small volume of data exchanged, wireless I / O radios use a technique known as "frequency hopping spread spectrum". This method is ideal for reducing interference caused by other radio signals in the area, and ensures extremely reliable transmission of I / O signals. The radios are available in 2.4 GHz or 900 MHz. By default, the system transmits its I / O status once per second. A "turbo mode" option can increase the refresh rate up to 10 times per second.
Consider the traditional method of installing a distributed I / O system wirelessly with Ethernet radios. However, this is a complicated operation, resulting in periods of inactivity that are always expensive. Thanks to ProSoft Technology's wireless I / O system, the costs are lower and the shutdown times disappear altogether.
What is the difference between wireless I / O and conventional Distributed I / O with Ethernet radios?
The second system, using Ethernet radios, requires operators in the field to support network communications and to program a data communication network. With ProSoft Technology's wireless I / O, this operation is unnecessary.
Also known as "wireless terminals", wireless I / O provides a simpler method of communication, designed to establish reliable and secure connections. Unlike data radios, the wireless I / O system requires no programming software or network protocols to configure. Wireless I / O radios are sold in pairs already programmed to connect with each other. The I / O signal sent between the radios uses 128-bit AES encryption to ensure that only the other coupled radio can read the information. Each I / O module reads the machine's physical signals - 24 VDC digital signals and 0 - 10 V or 4 - 20 mA analog signals - and then sends this information to the I / O module corresponding to the other termination . The corresponding module simply reproduces the signal on its output terminals. The digital I / O module has four inputs and four outputs, while the analog modules have two inputs and two outputs. The system is bidirectional, which means that each radio can send inputs and receive outputs. Each pair of radios can support 16 pairs of I / O modules, including 64 digital inputs and outputs or 32 analog inputs and outputs.
Given the small volume of data exchanged, wireless I / O radios use a technique known as "frequency hopping spread spectrum". This method is ideal for reducing interference caused by other radio signals in the area, and ensures extremely reliable transmission of I / O signals. The radios are available in 2.4 GHz or 900 MHz. By default, the system transmits its I / O status once per second. A "turbo mode" option can increase the refresh rate up to 10 times per second.